Categories
Contact
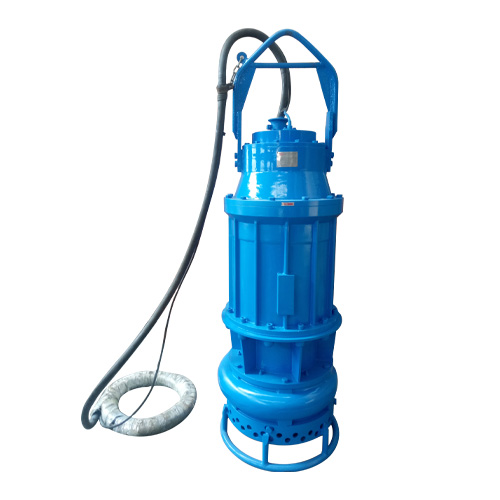

Submersible Sand Dredging Pump
The design of submersible sand dredging pumps incorporates several features that enhance their wear resistance.
Submersible sand dredging pumps are engineered to withstand the harsh conditions encountered in dredging operations, where abrasive particles constantly come into contact with the pump's internal components. The wear-resistant design is crucial for maintaining pump efficiency and extending its operational life, ultimately reducing downtime and maintenance costs.

One of the key design elements that contribute to wear resistance is the pump's impeller. Submersible sand dredging pumps often feature specially designed impellers with thick, robust vanes that can withstand the impact of abrasive particles. The impeller geometry is optimized to maintain a balance between efficient pumping and minimizing wear. Some designs incorporate recessed impellers, which create a vortex that helps keep abrasive particles away from the impeller edges, further reducing wear.
Another important aspect of wear-resistant design is the pump casing. The internal surfaces of the casing are often engineered with increased thickness in high-wear areas. Some manufacturers use replaceable wear plates or liners within the casing, allowing for easy maintenance and replacement of worn components without the need to replace the entire submersible sand dredging pump.
The clearances between rotating and stationary parts are also carefully considered in wear-resistant designs. Optimal clearances help minimize the grinding effect of abrasive particles trapped between components, reducing wear while maintaining pumping efficiency.
Additionally, the overall hydraulic design of the pump plays a role in wear resistance. Smooth flow paths and gradual transitions between pump components help reduce turbulence and localized high-velocity areas, which can contribute to accelerated wear.
Selection Chart of submersible sand dredging pump
Type | Capacity m3/h | Head m | Power kw | Speed r/min | Max particle size mm |
SS45-15-5.5 | 45 | 15 | 5.5 | 1460 | 13 |
SS50-10-5.5 | 50 | 10 | 5.5 | 1460 | 13 |
SS30-30-7.5 | 30 | 30 | 7.5 | 1460 | 13 |
SS50-26-11 | 50 | 26 | 11 | 1460 | 13 |
SS75-25-15 | 75 | 25 | 15 | 1460 | 13 |
SS150-18-18.5 | 150 | 18 | 18.5 | 980 | 32 |
SS200-12-22 | 200 | 15 | 22 | 980 | 45 |
SS60-46-30 | 60 | 46 | 30 | 980 | 21 |
SS150-30-30 | 150 | 30 | 30 | 980 | 21 |
SS300-20-37 | 300 | 20 | 37 | 980 | 28 |
SS200-30-45 | 200 | 30 | 45 | 980 | 36 |
SS500-15-45 | 500 | 15 | 45 | 980 | 46 |
SS250-35-55 | 250 | 35 | 55 | 980 | 36 |
SS600-15-55 | 600 | 15 | 55 | 980 | 46 |
SS350-35-75 | 350 | 35 | 75 | 980 | 28 |
SS500-20-75 | 500 | 20 | 75 | 980 | 25 |
SS200-60-90 | 200 | 60 | 90 | 980 | 14 |
SS400-40-90 | 400 | 40 | 90 | 980 | 28 |
SS600-30-110 | 600 | 30 | 110 | 980 | 28 |
SS1000-18-110 | 1000 | 18 | 110 | 980 | 50 |
SS500-45-132 | 500 | 45 | 132 | 980 | 28 |
SS1000-22-132 | 1000 | 22 | 132 | 980 | 50 |
SS650-52-160 | 650 | 52 | 160 | 980 | 28 |
SS780-50-185 | 780 | 50 | 185 | 980 | 38 |
SS800-55-220 | 800 | 55 | 220 | 980 | 38 |
SS1250-35-220 | 1250 | 35 | 220 | 980 | 45 |
SS1750-30-250 | 1750 | 30 | 250 | 980 | 55 |
SS2000-35-315 | 2000 | 35 | 315 | 980 | 60 |
High-Quality Materials
The choice of materials is crucial in ensuring the wear resistance of submersible sand dredging pumps. Manufacturers employ a variety of high-quality, durable materials that can withstand the abrasive nature of the pumped media. These materials are selected based on their hardness, toughness, and resistance to both erosion and corrosion.
One of the most commonly used materials in wear-resistant pump components is high-chromium white iron. This material, often containing 25-28% chromium, forms hard carbides that provide excellent resistance to abrasive wear. High-chromium white iron is frequently used in the construction of impellers, wear plates, and other components that come into direct contact with the abrasive slurry.

Another material often employed in submersible sand dredging pumps is duplex stainless steel. This material offers a combination of high strength, good corrosion resistance, and moderate wear resistance. Duplex stainless steel is particularly useful for pump shafts and other structural components that require both strength and corrosion resistance.
For extremely abrasive applications, some manufacturers use specialty materials such as tungsten carbide or ceramic composites for critical wear components. These materials offer exceptional hardness and wear resistance, albeit at a higher cost.
The selection of materials often involves a balance between wear resistance, cost, and other factors such as weight and manufacturability. Advanced materials may offer superior wear resistance but can significantly increase the pump's cost and weight. Manufacturers typically offer different material options to suit various applications and budgets.

Hardened Surfaces
In addition to using wear-resistant base materials, many submersible sand dredging pumps incorporate surface hardening techniques to further enhance their durability. These techniques involve treating the surface of pump components to increase their hardness and wear resistance without affecting the properties of the underlying material.
One common surface hardening method is hard-facing, also known as hardfacing or hard surfacing. This process involves applying a layer of wear-resistant material to the surface of pump components using welding techniques. The hard-facing material is typically a specially formulated alloy that offers superior wear resistance compared to the base material. Common hard-facing alloys include tungsten carbide composites, chromium carbide composites, and various iron-based alloys.
Hard-facing can be applied selectively to high-wear areas of the pump, such as the impeller vanes, volute cutwater, and suction liner. This targeted approach allows manufacturers to optimize the balance between wear resistance and cost.
Another surface hardening technique used in some submersible sand dredging pumps is nitriding. This process involves diffusing nitrogen into the surface of steel components at elevated temperatures. Nitriding creates a hard, wear-resistant layer on the surface of the material without significantly changing its dimensions. This technique is particularly useful for components that require precise tolerances, such as shafts and bearings.
Some manufacturers also employ thermal spraying techniques to apply wear-resistant coatings to pump components. These coatings, which can be made from materials such as tungsten carbide or chromium oxide, provide an extremely hard and durable surface layer that can significantly extend the life of pump components.
The choice of surface hardening technique depends on factors such as the base material, the specific wear requirements of the application, and the geometry of the component. Often, a combination of techniques may be used to achieve optimal wear resistance across different parts of the pump.
Mechanical Sealing
The sealing system is a critical component in submersible sand dredging pumps, responsible for preventing the ingress of abrasive particles into sensitive areas of the pump, such as the bearings and motor. Wear-resistant mechanical seals are essential for maintaining the integrity and performance of the pump over time.
Modern submersible sand dredging pumps often employ multiple sealing arrangements to provide robust protection against abrasive particles. A typical configuration might include:
1. Primary mechanical seal: This seal is in direct contact with the pumped media and is designed to withstand the abrasive environment. It often uses hard-facing materials such as silicon carbide or tungsten carbide for the seal faces to provide excellent wear resistance.
2. Secondary mechanical seal: This seal provides an additional barrier against any particles that may pass the primary seal. It may use slightly less wear-resistant materials as it is not in direct contact with the abrasive slurry.
3. Labyrinth seals: These are non-contact seals that create a tortuous path for particles, making it difficult for them to enter sensitive areas of the pump.
4. Seal flushing systems: Many submersible sand dredging pumps incorporate a clean water flushing system that continuously flushes the mechanical seals, helping to cool them and prevent the ingress of abrasive particles.
The design of the sealing system also considers factors such as shaft deflection, thermal expansion, and pressure variations to ensure consistent performance under various operating conditions. Advanced sealing technologies, such as balanced mechanical seals and cartridge-style seals, are often employed to enhance reliability and simplify maintenance.